LitOUTer
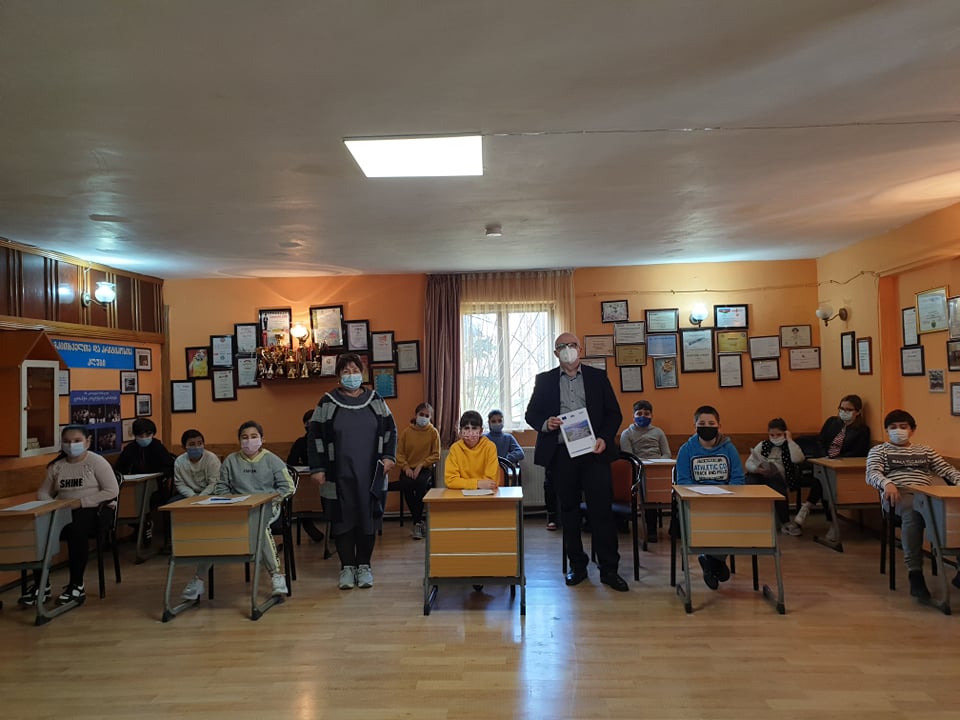
N(N)LE International Business and Economic Development Center carry out implementation EU funded project on “Raising Public Awareness and Reducing Marine Litter for Protection of the Black Sea Ecosystem” (LitOUTer)” with lead partner Karadeniz Technical University- Marine Science Faculty from Turkey and partners: Non-governmental environmental organization Mare Nostrum and National Institute for Marine Research and Development “Grigore Antipa” from Romania; Institute of Oceanology – BAS and Black Sea NGO Network from Bulgaria- in the framework of Black Sea Basin Program 2014-20.
Overall objective of the project is raise awareness of public and local decision makers and all stakeholders like: Environmental agencies, Maritime Agency, Businesses, Fishing companies, Environmental NGO’s, Research Institutions and Universities, Students, schoolchildren, General Public, Housewives from the target region.
The Black Sea is a fragile marine environment, countries continue to dump their pollutants/ wastes/ litters via river basin discharges. A solution coming from a single country is worsted nothing while litter carrying by rim current flow all around the Black Sea coasts. By this approach, four coastal countries should be in cross border cooperation under this project to improve the permanent solution to reduce litter discharges to the Black Sea. We, as partners, believe that LITTER “OUT” is not a dream for the Black Sea environment.
Specific Objectives:
Raising awareness and responsibility of the stakeholders to reduce marine litter:
Organization of training, meetings, interviews, mass media programs, round table meetings and workshops, leaflets, brochures and posters for the target groups at different age and social levels by providing various awareness materials; animation film and toys for children, field works for students, local decision makers and local citizens, questionnaires for data collection and user friendly GIS based model application;
Determination of the proportions of the potential sources for the marine litters:
There are many different sources for the marine litter. Determination and management of waste must be the first step for the mitigation, reduction and re-use of them. Strategically, reduction and recycling of the wastes at the sources are more economic, harmless for the environment and manageable by governors. Determination of the marine litter sources, ways of transport, and each country will sample their identified area for field studies. The ratio of the litter sources will be classified.
Development of methods for mitigation and determination of cleaning strategies of marine litters:
Methodologies for reducing of marine litters must be organized by governors and started up in houses/villages. Data from responsible institutions will be analyzed quantitatively. The results of this analysis will be guide for local authorities to improve alternative collection methods (more bin, more waste collecting trucks, burying organic waste, recycling). Model outputs will demonstrate accumulation areas in the coast and guide us to produce solutions to remove/mitigate solid wastes. Many national and international organization describe what marine litter is? According to the UNEP:“Marine litter is any persistent, manufactured or processed solid material discarded, disposed of or abandoned in the marine and coastal environment.”
We also produce a description about litter like “A thing is produced for a purpose then not used anymore is “litter”. If it reaches to the sea then is named “marine litter”. Here is the most important dilemma that human must be decide if recycle them or accumulate them under the sea.
The project team believe that, the target stakeholder groups will have an idea about litter at the end of the project. This will be the best benefit of the project to the local people in the project area and other people who visit digital media/portal of the project.
In the project, litter transportation ways with many vectors will demonstrate. This action will raise the stakeholder’s awareness which is crucial step for reducing marine litter at the source. They will realize that, unconscious throw and/or uncontrolled dumped solid wastes which are moved along the rivers and finally reached to the sea basin.
Proposed project will be held by sub-regional basis (limited with the partners' borders). With this project, all partners will test the efficiency of current instruments, programmes and initiatives to protect the Black Sea. Each partner country will work in their own coast and hinterland about 50 km inside from the coast along the river basin. During the project progressing period, partners will analyses their areas by means of;
- Waste collecting facilities,
- Amount of collected solid wastes (data from responsible institution),
- Training and litter collection activities on coastal areas (involving all partners in their sampling areas)
- Training and litter collection activities in the research vessels (Turkish and Bulgarian coasts)
- Workshops, meetings, questionnaires (two times; at the beginning and end of the project), symposium for raising awareness of the stakeholders and transferability of project outputs.
After a clear understanding of the meaning of litter, we can also find out a solution together with the collaboration of the neighbors. Project partners have knowledge and experience in the Black Sea and solid waste pollution.
Type and amount of litter of the four countries will be analyzed in case of social, cultural, welfare of the targeted groups. In the next step, different awareness material and training methods will be selected for the training of different target groups. On the other hand, we will learn whether cultural differences have an effect or not on their reaction to minimize marine litter pollution.
At present, marine litter is a real challenge for the Black Sea countries because of a lack of knowledge and financial support and also different social and cultural differences. Collection, separation, and recycling systems are not enough to diminish and solve the problem.
Education, training, information, and knowledge are vital components to raise the awareness of the public and decision-makers to combat with marine litter problem. Education/training on sources and possible effects (may kill, injure, cause pain, suffer and cause important economic losses) of marine litter and ways of reducing their impacts at source needs effective cooperation at different levels with many visual materials and methods. Stakeholders should be warned about the benefits of litter separation on a source in order the reduce ongoing impacts. It will be cheaper, sustainable, and successful than any cleaning and rehabilitation operations.
Although importance and dimensions of the marine litter problem has well known, the main challenges for reducing marine litter are, lack of political willingness, financial and technological requirements ,lack of awareness, increase industrial products which have required packaging, not enough collecting and storing capacity of the solid wastes, no/very few recycling planning facilities around BS countries. Meanwhile, quantity of litters has increased in line with the use of industrial products in wider scale by years
This project is neither scientifically creative nor ambitious about discovering new technologies to save our world forever, but, this project is a collaborative study with our neighbors to reduce marine litter in order to saving our Black Sea marine environment.
Scientists and decision makers know what the sources of the marine litters are, on the other hand, public, villagers, students never realize what throwing litters fate and effects on their environment and their life. For example, public who live from 50 km inside from coast never realized that how their solid wastes can reach to the sea by runoff or atmospheric transportation. In the project, we will demonstrate, the reality of the litter transportation ways with many vectors. This action will raise the stakeholder's awareness which are crucial step for reducing marine litter at the source.
A GIS based hydrodynamic-litter modified model is another innovative approach for raising public awareness about marine litter behavior with currents, waves and wind. Unconscious thrower and/or uncontrolled dumped solid wastes which are moved along the rivers and finally reached to the sea basin will be demonstrated by model with different scenarios. The output of model will be integrated in GIS maps. The results will be more user friendly and more understandable and more colorful for the stakeholders. They will understand easily, what happens if they throw, how litters reach to the sea and accumulate.
Training activities should start at early ages at home, then continue in schools and finally in the society. If we choose children, and young man and women’s as a target group for training on the litter pollution and their effects on marine ecosystem and human health, we believe that success level of the project sustainability will be the highest. The results may not been noticed hundred percent during the project but absolutely will be successful.
In order to reach these targets several awareness raising methods will be applied to explain what the marine litter is, why we need to reduce, consequences for the environment, and the benefits of reducing wastes i.e. plastics, papers by personal communications, public meetings/debates with community members, structured training programmes with administrations, maritime businesses, other sectors, public utilities etc. (on topics linking with marine litter management practices, the Marine Strategy Framework Directive and the Maritime Spatial Planning Directive, MSFD and marine protected areas; the ecosystem approach in practice; linking the Regional Seas Conventions to production of regional Plan for marine litter management).
Furthermore, we aimed to use web based sources ( articles, project database, maps, handbooks, media/social media publications, mass media interviews and articles in newspapers, magazines and electronic publications accessible via project web site, social media campaigns), strategic partnerships and alliances (transfer of knowledge/experience and advocacy), and pilot application/demonstration activities (trawling for marine litter and/or similar activities performed by the scientific institutes for demonstration and awareness).
Raising awareness of public and local decision makers are crucial point for reducing, managing of river and marine litters in the coastal area, in the sea bed and cross-border transfer. Visual and audiovisual materials play an important role in raising awareness training and campaigns with all relevant stakeholders. Animation and toys for children, leaflets, videos, workshops and symposium will be helpful to explain the effects of the litter in the marine environment to the public, in general. GIS based hydrodynamic model will also help to understand the cross-border movement of the litters. Project primarily focuses on identification, management and mitigation of the waste sources and raising the awareness of the citizens.
In general, marine litter is distributed by currents along the coastline and across the region. After being environmental problem, special care was given to marine litter case in Turkey. Institutionally we paid more attention to marine litter problem in the BS coast of Turkey. In September 2004, first marine litter research was started together with KTU, local governments and NGOs (Association of Environmental Cultural Entrepreneurs, Society for the Protection of Natural and Historical Values ) by the grant of UNDP-GEF. In September 2015, KTU was carried out a survey on marine biodiversity and marine litter in the Eastern Turkish Black Sea coast. The results of these projects are quite stunning as to show the dimensions of the marine litters and their accumulations around major polluted deltas, fishing ports and small shelters. After the implementation of this project we expect to: - clarify rate of solid waste discharges from rivers, - identify degree of the pressures from different sources (i.e. rivers, fisheries and fish farms, tourism, shipping, industry), - raise awareness of the public and decision makers by using visual and audio-visual materials, web based sources, mass/social media campaigns and interviews, meetings, symposium and questionnaires, - convince housewives to separate litters (paper, glass, plastics, tin as initials) at home for further collection and recycling processes, - teach benefits of organic wastes to use them as fertilizer in their small gardens, - coordinate municipalities to start separated litter collection and transfer to recycling plants, - improve new generations responsible for saving their environment and future, Expected results from the planned activities will be useful to improve welfare of the BS citizens and sustainable ecosystem for the living resources across basin through joint reduction of marine litter in coordination to implement common actions by transforming fragile environment to good state.
Pls find link of the project website: https://litouterproject.eu/
IASON
N)LE International Business and Economic Development Center is implementing EU funded project on “Invasive Alien Species Observatory and Network Development for the Assessment of Climate Change Impacts in Black Sea Deltaic Protected Areas (IASON)” with lead partner The Danube Delta National Institute for Research and Development from Romania and partners: Danube Delta Biosphere Reserve Authority from Romania; Institute of Marine Biology of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine from Ukraine; International Hellenic University – Department of Forest and Natural Environment Sciences from Greece; Karadeniz Technical University – Faculty of Marine Sciences from Turkey- in the framework of Black Sea Basin Program 2014-20.
Species’ geographic distribution is the outcome of the interaction between their niches and environmental conditions. Among these, climatic factors are well known that influence species growth and their worldwide geographic distribution. Moreover, climate change is expected to cause shifts in the geographic distribution of species as their optimal habitat will likely shift as a result of the rearrangement of the climate zones.
The distribution of plant and animal species outside their natural distribution is a common phenomenon in a large number of countries all over the world. In the past, the humankind has greatly benefited from the introduction of alien species (e.g. potatoes and maize in Europe, etc.) and this trend is likely to continue. Among these species, a large number has been naturalized and now can be found in natural habitats. However, some of them have become invasive, having multiple ecological, economic and human health impacts. The distribution of invasive alien species (IAS) is mainly climate driven and this is why they can be found in a number of countries that are far from their native distribution range. Specifically regarding the impacts that IAS can cause, they not only represent a threat to native fauna and flora (IAS are globally considered as the second major threat to biodiversity), but can also result in major disruption to ecosystem health, with resulting damage and loss of goods and services. Increasing pressures on ecosystems, caused mainly by destruction of habitats, spread of IAS, over-exploitation and pollution, are weakening ecosystem resilience and ability to adapt to new conditions under climate change and thus continuously declining capacity for providing ecosystem services.
Under the global changing environment, the Black Sea is found in between the European and Asian crossroad and in the transition between the Mediterranean and North. A great number of stakeholders have developed economic activities around the Black Sea coastline, especially at the deltas, which are known for their density in population and growth potential (such as fishing, fisheries and aquacultures, tourism and recreation, farming etc). Historically, the Black Sea was under the invasion of alien species from the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea due to various reasons. Invasive Alien Species (IAS) is the central point on which this project makes focus, because if not sufficiently monitored and assessed they may alter dramatically not only the ecosystem balance, but also a range of already well-established socio-economic activities. The overall objective of the project is to establish and perform joint monitoring actions on IAS in the Black Sea deltaic ecosystems of five countries (Georgia, Greece, Ukraine, Romania and Turkey) and assess their response under current and predicted climatic conditions.
Overall Objective of the project is:
To establish, perform and communicate joint monitoring actions on Invasive Alien Species (IAS) in Black Sea deltaic ecosystems and assess their response under current and predicted climatic conditions.
The specific objectives of the project are to:
- To develop and implement the joint monitoring and risk assessment procedures on IAS in the project nature protected areas and motivate and assist countries in creating their IAS inventories.
- To improve long-term cross-border collaboration, information and research capacity through using innovative technologies on IAS monitoring.
- To improve cooperation on IAS monitoring through the involvement of the public at various levels of the project.
Main results of the project will be to:
- Gain baseline data on IAS in the project deltaic areas, under current and predicted climatic conditions, through the implementation of joint cross-border monitoring and evaluation.
- The establishment of an organizational structure (Observatory) through which Information and communications technology (ICT) services will be provided not only on IAS monitoring and assessments (information & research capacity) but also on networking with/and engaging citizens towards improving and using updated results of the project (institutional capacity).
- Cross-border collaboration and exchange of developing and implementing information and communication activities, at all levels of society (education, managers, policy makers, local community).
PARTNERS
Romania: The Danube Delta National Institute for Research and Development -
Coordinator
Romania: Danube Delta Biosphere Reserve Authority
Ukraine: Institute of Marine Biology of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine
Greece: International Hellenic University – Department of Forest and Natural Environment
Sciences
Turkey: Karadeniz Technical University – Faculty of Marine Sciences
Georgia: International Business and Economic Development Center- IBEDC
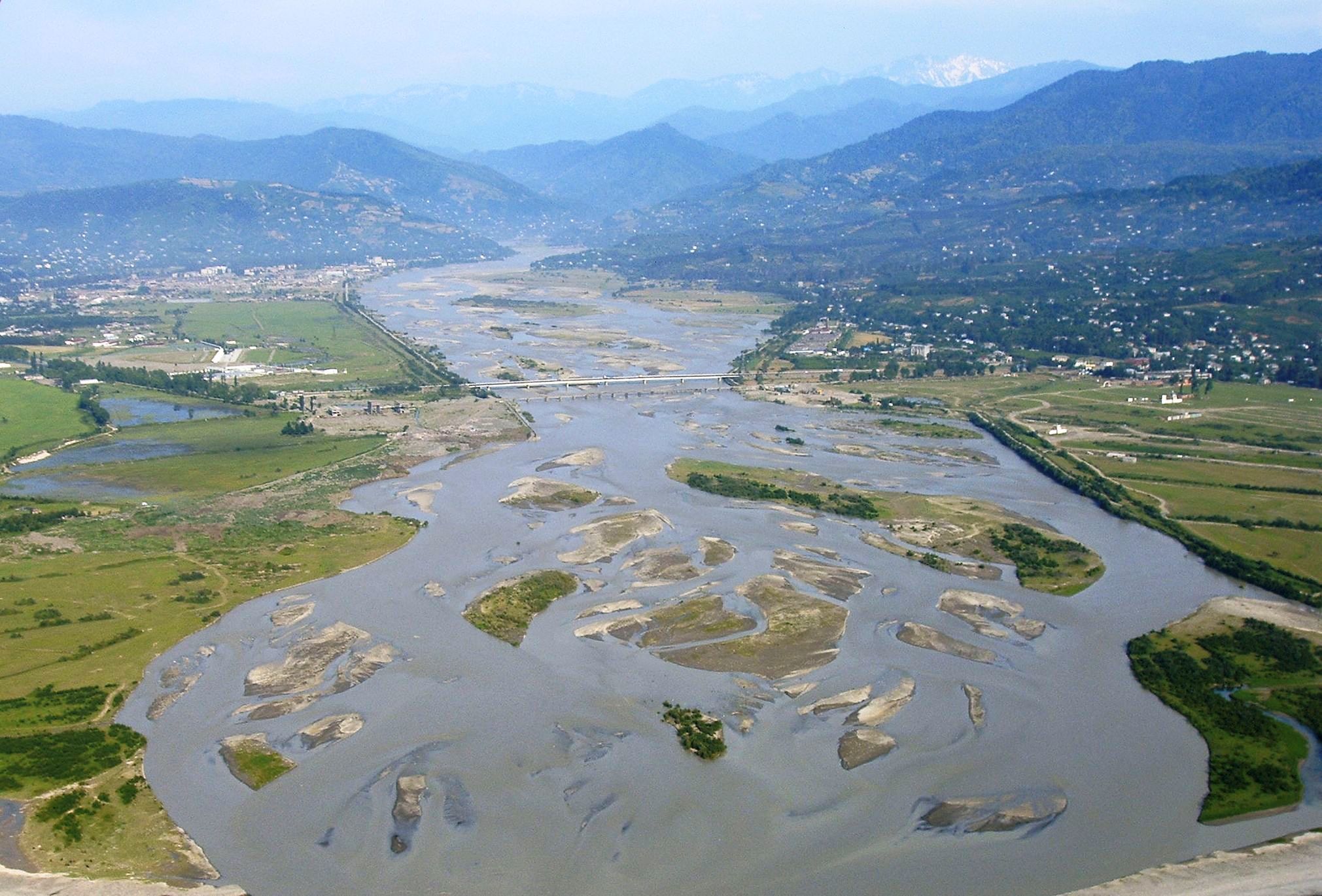
The monitoring area of the IASON project consists of five distanced deltaic study areas (of the following rivers) which share common characteristics, but also have different environmental management backgrounds.
-Danube (Ukraine & Romania)
-Nestos (Greece)
-Kızılırmak or Halys (Turkey)
-Chorokhi & Kolkheti (Georgia)
Why deltaic ecosystems?
All deltaic ecosystems are densely populated all over the world and traditionally support a great number of economic activities. According to reports from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, the climate-related changes during the 21 st century will include acceleration in the sea level rise, further rise in sea surface temperature, more extreme weather events and storm surges, altered precipitation and ocean acidification. Deltas are inherently vulnerable ecosystems with their biological communities being adaptable in this situation. However, the climate change could result in 50% increase of delta surface areas that are vulnerable to flooding and in the trends of progressive warming to increasing of the water temperature. At coastal zones and deltas these climate-related changes are expected to have a range of physical, economic and social impacts.
The multifaceted character of the project area – deltaic ecosystems of different biogeographical zones, different protection status & management, cross-border or one- country owned – creates major challenges in regard to IAS management in a climate changing future in the Black Sea region. Under this assumption, IASON project is structured in a way that all challenges areapproached under an integrated and cross-border manner.
In particular, the project approach will consist of the following characteristics:
1.Joint and compatible cross-border monitoring & evaluation methodologies.
- Development of IAS lists under encompassing literature review and stakeholder’s values at the local scale
- Development of common monitoring protocols and IAS risk assessment methodology
- Climatic analysis and future climatic projections, that will also provide analysis at the local (delta scale) and biogeographical scale
- Mapping in protected areas under Natura 2000 requirements, so as non-EU countries become familiar with EU monitoring principles
- The establishment of baseline data after risk assessments on IAS that refer exclusively to the deltas of the project area
2.Interaction between researchers and relevant stakeholders.
- Information programmes at the local level including educational activities, as well as public events that pursue engagement of local stakeholders and the general public so as they may contribute to recording IAS occurrences through the use of ICT tools.
- Interaction of citizens with Observatory researchers through the Living Lab platform.
- Profit from the project results and in particular form IAS risk assessments in the deltas under current and predicted climatic conditions.
3.Availability and cross-border interoperability of updated online information systems & tools. The development of the ICT tools through the operation of the Observatory is expected to create a number of communication & information overlaps. Access on online data and information will strengthen the two-way interaction and feedback that is needed both between researchers and citizens as well as at a cross-border level. Also, the establishment of the meteorological stations and their linking with the ICT tools of the Observatory will put forward the provision of a long-term information flow for the benefit of research and society under a climate change future.

Anadara kagoshimensis

Beroe

Gambusia affinis

Rapana venosa

Pseudorasbora parva
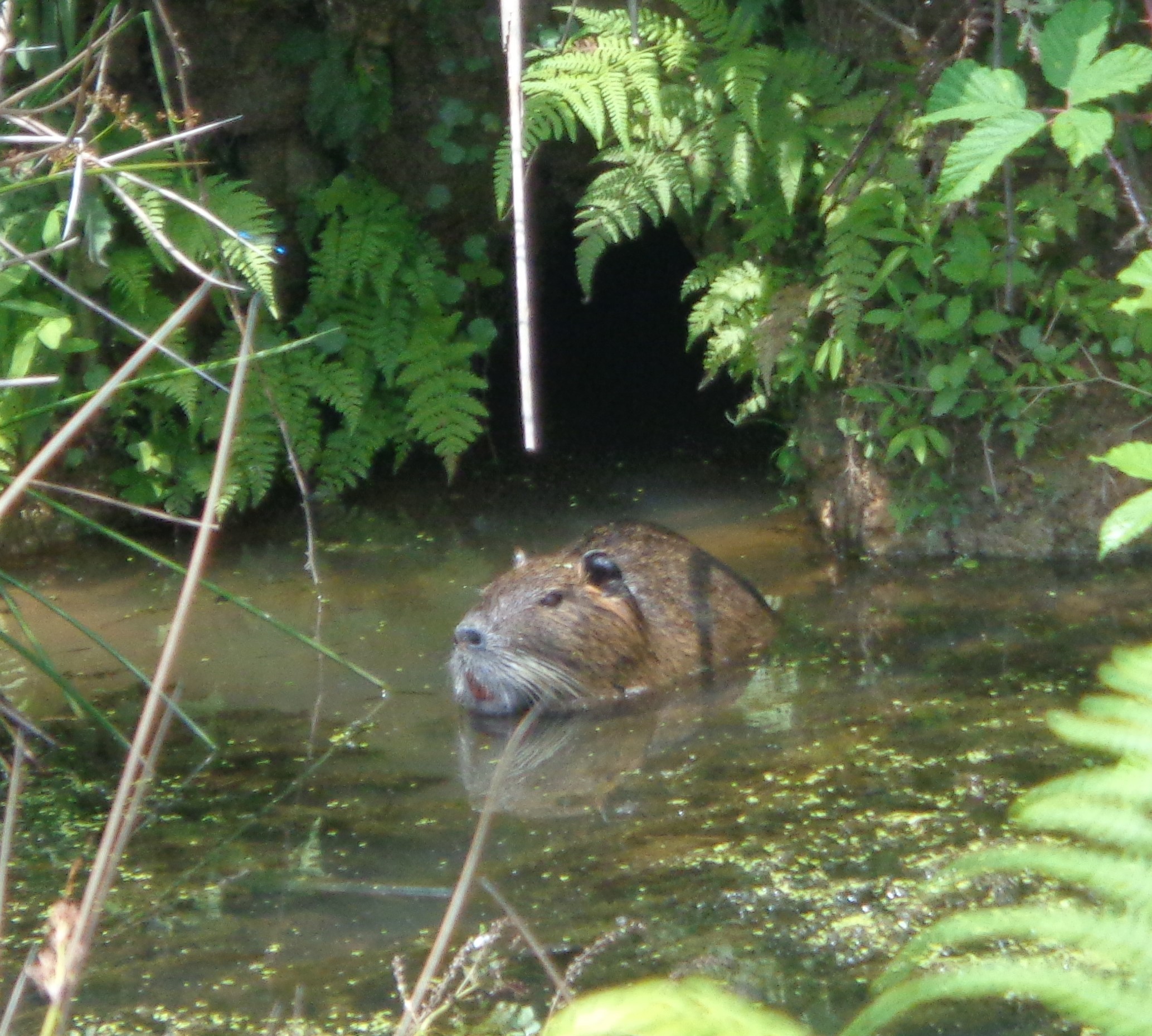

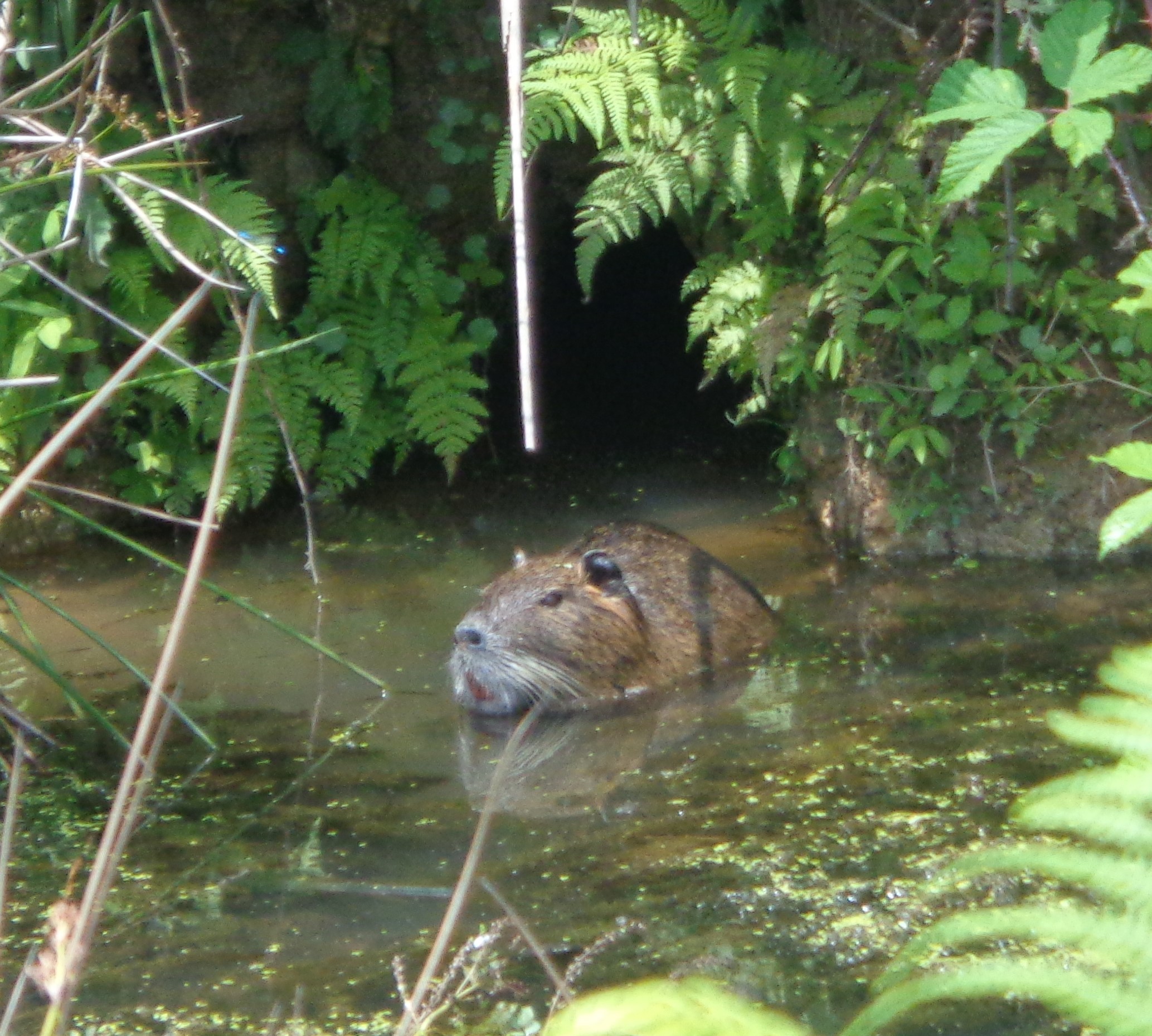
Myocastor coypus